Embark on a journey into the world of Portfolio Diversification Strategy, where we unravel the secrets to optimizing your investment portfolio with a mix of assets. Get ready for a deep dive into the realm of diversification and its impact on your financial success.
Delve into the various asset classes, benefits, and strategies that can revolutionize your investment approach.
PORTFOLIO DIVERSIFICATION STRATEGY
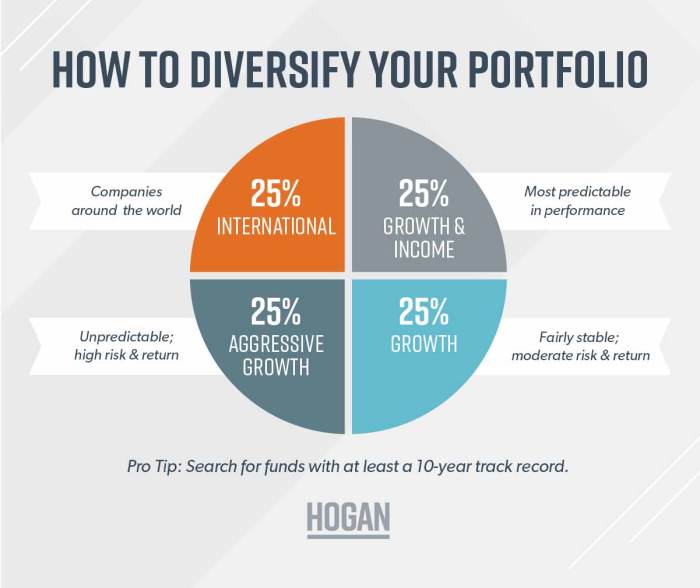
Portfolio diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and improve overall return on investment.
Examples of Asset Classes
- Stocks: Investing in shares of publicly traded companies.
- Bonds: Purchasing debt securities issued by governments or corporations.
- Real Estate: Investing in properties or real estate investment trusts (REITs).
- Commodities: Investing in physical goods like gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products.
- Alternative Investments: Including assets like hedge funds, private equity, or cryptocurrencies.
Benefits of Portfolio Diversification
- Risk Reduction: Diversification helps mitigate the impact of volatility in any single asset class.
- Improved Returns: By spreading investments, diversification can potentially enhance overall returns and reduce the impact of poor performance in one area.
- Stability: A diversified portfolio can provide greater stability during market fluctuations or economic downturns.
- Opportunity for Growth: Different asset classes have unique growth patterns, providing opportunities for capital appreciation.
PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT

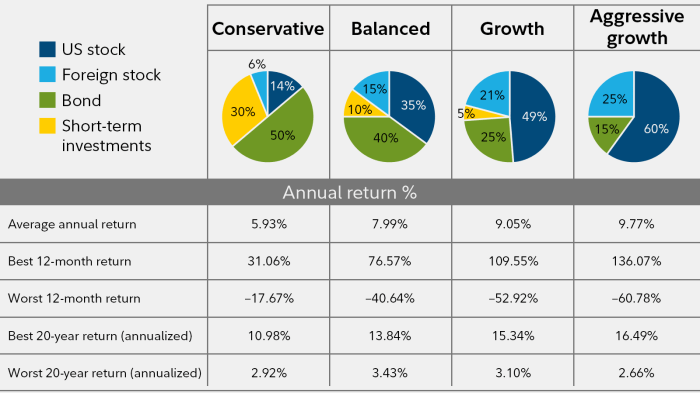
Portfolio management is the art and science of making decisions about investment mix and policy, matching investments to objectives, asset allocation for individuals and institutions, and balancing risk against performance. It plays a crucial role in maximizing returns while minimizing risk.
Role of Risk Assessment in Portfolio Management
Risk assessment is a key component of portfolio management as it helps investors understand the potential risks associated with their investments. By evaluating risk, investors can make informed decisions about asset allocation and diversification to protect their portfolios from potential losses. It involves analyzing the volatility and correlation of different assets to create a balanced portfolio that aligns with the investor’s risk tolerance.
Active vs. Passive Portfolio Management Strategies
- Active Portfolio Management: Involves frequent buying and selling of securities in an attempt to outperform the market. Portfolio managers actively make investment decisions based on market trends, economic forecasts, and individual security analysis. This strategy aims to generate higher returns than the market average, but it also comes with higher costs and risks due to the frequent trading.
- Passive Portfolio Management: Involves investing in a predetermined mix of assets to match the performance of a specific market index. Portfolio managers do not actively make investment decisions but instead focus on maintaining the portfolio in line with the index. This strategy aims to replicate the market returns at a lower cost compared to active management, as it involves minimal trading and lower management fees.
In conclusion, Portfolio Diversification Strategy is a powerful tool that can significantly enhance your investment outcomes and mitigate risks. By diversifying your portfolio intelligently, you pave the way for a more secure and prosperous financial future.
Question Bank
Why is portfolio diversification important?
Portfolio diversification helps spread risk across different investments, reducing the impact of a single asset’s performance on your overall portfolio.
How many asset classes should I include in my diversified portfolio?
The number of asset classes to include depends on your risk tolerance and investment goals, but typically, a well-diversified portfolio should have exposure to at least 3-4 different asset classes.
What are the key differences between active and passive portfolio management?
Active portfolio management involves frequent buying and selling of assets in an attempt to outperform the market, while passive management aims to match the performance of a specific market index with minimal trading.






