
Active vs Passive Portfolio Management sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail with casual formal language style and brimming with originality from the outset.
In the realm of investment management, the choice between active and passive strategies can significantly impact portfolio performance and risk management. Let’s delve deeper into the intricacies of these approaches to understand their nuances and implications.
Active vs Passive Portfolio Management
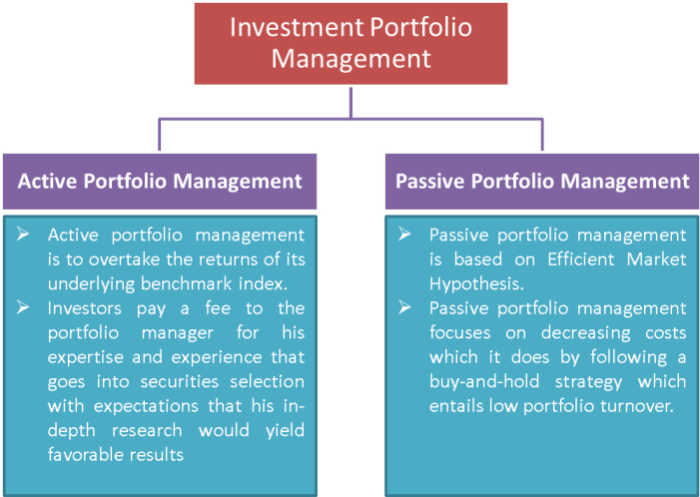
Active and passive portfolio management are two distinct approaches to managing investment portfolios. Active management involves a hands-on approach where portfolio managers actively make decisions to try and outperform the market. On the other hand, passive management involves tracking a specific market index or benchmark without making frequent changes to the portfolio.
Investment Strategies
Active management strategies include stock picking, market timing, and sector rotation. Portfolio managers actively analyze market trends, economic data, and company performance to make investment decisions aimed at generating higher returns than the market.
Passive management strategies, on the other hand, involve investing in index funds or ETFs that aim to replicate the performance of a specific market index, such as the S&P 500. These strategies require less frequent trading and tend to have lower fees compared to active management.
Benefits and Drawbacks
- Active Management:
- Benefits:
- Potential for higher returns than the market
- Ability to capitalize on market inefficiencies
- Drawbacks:
- Higher fees and expenses
- Increased risk of underperforming the market
- Benefits:
- Passive Management:
- Benefits:
- Lower fees and expenses
- Consistent returns with the market
- Drawbacks:
- No opportunity to outperform the market
- No active management to react to market changes
- Benefits:
Portfolio Diversification
Portfolio diversification is a strategy that involves spreading your investments across different asset classes to reduce risk and optimize returns. By diversifying your portfolio, you can minimize the impact of market fluctuations on a particular investment and increase the overall stability of your investment portfolio.
Examples of Asset Classes in a Diversified Portfolio
- Stocks: Investing in shares of companies from various industries and regions.
- Bonds: Including government bonds, corporate bonds, and municipal bonds in your portfolio.
- Real Estate: Investing in properties or Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs).
- Commodities: Adding assets like gold, silver, oil, or agricultural products to diversify your portfolio.
- Alternative Investments: Including assets like hedge funds, private equity, or cryptocurrencies.
How Diversification Helps in Managing Risk and Enhancing Returns
Diversification allows investors to reduce the overall risk of their portfolio by spreading investments across different asset classes. If one particular investment performs poorly, the impact on the entire portfolio is minimized as other investments may perform well. This risk mitigation strategy helps protect against significant losses that could result from having all investments concentrated in a single asset class.Moreover, diversification can potentially enhance returns by capturing the performance of different asset classes that may be moving in different directions.
When one asset class underperforms, another asset class may be experiencing growth, balancing out the overall returns of the portfolio. This can lead to a more stable and consistent investment performance over the long term.
Active Portfolio Management Strategies

Active portfolio management involves strategies such as market timing and stock picking, where portfolio managers actively make decisions to try to outperform the market.
Market Timing
Market timing is a strategy where portfolio managers try to predict the future movements of the market to buy and sell assets at the most opportune times. This strategy involves making decisions based on economic indicators, market trends, and other factors to capitalize on potential market fluctuations.
Stock Picking
Stock picking is another active portfolio management strategy where managers select individual stocks that they believe will outperform the market. This involves conducting thorough research and analysis on companies to identify undervalued or high-growth potential stocks.
Real-World Examples
One famous example of successful active portfolio management is Warren Buffett, known for his stock-picking prowess and value investing strategy. Buffett’s investment in companies like Coca-Cola and American Express has consistently outperformed the market over the years. Another example is Peter Lynch, who managed the Fidelity Magellan Fund and achieved remarkable returns through his stock-picking approach and in-depth research on companies.
Passive Portfolio Management Strategies
Passive portfolio management involves investing in a diversified portfolio of securities that closely mirrors a specific market index. This approach aims to achieve returns that are in line with the performance of the chosen index, rather than attempting to outperform the market through active trading.
Index Tracking
Passive management strategies primarily focus on index tracking, where the portfolio is constructed to replicate the composition and weighting of a particular market index. By holding a mix of assets similar to those in the index, passive managers seek to match the overall returns of the market.
- Passive managers do not engage in frequent buying and selling of securities, as their goal is to mimic the benchmark index.
- Index funds and exchange-traded funds (ETFs) are common vehicles used for passive investing, offering broad exposure to various asset classes.
- By following a passive approach, investors can benefit from low costs and reduced portfolio turnover compared to active management.
Cost Comparison
When it comes to costs, passive management generally incurs lower fees than active management. Since passive strategies involve less frequent trading and rely on index replication, the expenses associated with research, analysis, and portfolio turnover are significantly reduced.
- Passive funds typically have lower management fees and operating expenses compared to actively managed funds.
- With fewer transactions taking place in passive portfolios, investors can also save on brokerage costs and taxes associated with capital gains.
- Over the long term, the cost efficiency of passive management can contribute to higher net returns for investors, especially in a low-return environment.
As we conclude this discussion on Active vs Passive Portfolio Management, it becomes evident that both strategies have their unique advantages and drawbacks. By grasping the essence of each method, investors can make informed decisions to optimize their investment objectives effectively.
FAQ Insights
What is the main difference between active and passive portfolio management?
Active management involves frequent buying and selling of securities in an attempt to outperform the market, while passive management aims to mirror the performance of a specific market index through minimal trading.
How do active managers aim to outperform the market?
Active managers employ strategies like market timing and stock picking to capitalize on market inefficiencies and generate higher returns than the overall market.
What are the benefits of passive portfolio management?
Passive management typically has lower costs, reduced portfolio turnover, and can offer broad market exposure without the need for constant monitoring.





